Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Descriptive Statements:
- Analyze the physical properties of water, including energy changes that occur in the hydrologic cycle.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the chemical properties of water and how water chemistry changes during the hydrologic cycle.
- Analyze the interrelationship of the hydrosphere and other Earth systems.
Sample Item:
During which of the following phase changes would the greatest amount of energy per
gram of water be released to the environment?
- Water evaporates from a reservoir on a hot and dry day.
- On a cold fall morning, frost forms on a lawn.
- Ice sublimates on a very cold and dry day.
- On an early summer morning, dew forms on a field.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
B. This question requires the examinee to analyze the energy changes
that occur as water changes phase. Energy must be added to water to vaporize liquid
water or melt ice, however energy is given off by water when the processes are reversed.
Frost is a particular case in which water vapor is converted to ice without passing through
a liquid phase. It is because of this that the formation of frost releases more heat than
the phase change from gas to liquid that occurs during the formation of dew.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the origins and physical structures of ocean basins and different types of coastlines.
- Analyze the physical and chemical characteristics of ocean water.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the causes and characteristics of ocean currents, waves, and tides.
- Analyze the characteristics, formation, management, and use of geologic and biological marine resources.
Sample Item:
The continental shelf of the East Coast of the United States comprises:
- thin deposits of marine mud overlying the remnants of ancient limestone reefs.
- salt deposits alternating with layers of basalt.
- shifting sandbars overlying the eroded remains of uplifted oceanic crust.
- thick layers of sand, silt, and mud overlying granitic crust.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
D. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the
physical structure of the continental shelf. The continental shelf is the submerged,
gently sloping section of the continental margin that stretches from the coastline to the
beginning of the much steeper continental slope. Abundant sediments, primarily from the
erosion of the adjacent continent, can accumulate to a thickness of several kilometers.
These sediments typically range from coarser material that is deposited near the coastline
to silt and mud that accumulate farther out on the continental shelf.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the properties of surface water, factors affecting stream flow, the dynamics of drainage systems, and the functions of watersheds.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the properties of groundwater, including factors affecting the movement, infiltration, extraction, and quality of groundwater resources.
- Analyze geologic factors affecting the availability, use, and management of freshwater resources.
Sample Item:
A mature river system with a gentle grade flowing over coastal plain sediments is likely
to have a configuration most similar to which of the following illustrations?
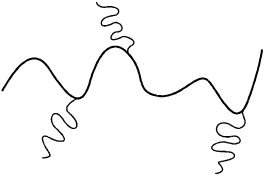

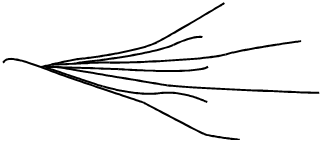

Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
A. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the
characteristics of river drainage systems. A mature river flowing across a coastal plain
composed of sediments will typically develop a meandering pattern due to the gentle slope
of the coastal plain, the slow flow velocity of the river, and the nature of the fine-grained
sediments through which it carves its channel.

