Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the sun's structure, life cycle, and energy production.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics and evolution of different types of stars, including the process of nucleosynthesis.
- Recognize the characteristics of the Milky Way Galaxy and other types of galaxies.
- Analyze theories of the origin and nature of the universe and the characteristics of black holes, dark matter, supernovas, and quasars.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the technology used to explore, and the evidence used to understand, the solar system, stars, extrasolar planets, galaxies, and the universe.
Sample Item:
Which of the following physical characteristics of a main-sequence star is the most
important factor in determining its luminosity?
- total mass
- size of the corona
- chemical composition
- strength of the magnetic field
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
A. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the
physical characteristics of stars. The luminosity of a star is a measure of the amount
of energy it radiates each second. Based on research conducted during the 1920s, the
astrophysicist A.S. Eddington discovered that the luminosity of a main-sequence star is
determined by its mass. Eddington's discovery is the basis of the mass-luminosity
relationship L = M 3L equals M cubed, where the luminosity of a main-sequence
star is equal to the star's mass cubed. Analysis of the energy emitted by a star
continues to be an essential tool that astronomers use to deduce stellar properties,
including composition, temperature, size, and mass.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the origin and structure of the solar system.
- Recognize the position and characteristics of the planets and their satellites.
- Recognize the origin and characteristics of comets, asteroids, and meteors.
- Recognize the physical and mathematical models and laws that describe the motions of objects in the solar system.
Sample Item:
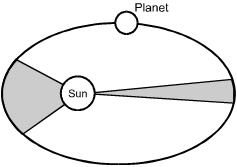
The orbit is elliptical with the sun at one focus of the ellipse. On either side of the sun along the long axis of the ellipse, there is a symmetrical area shaded gray around the long axis. At the end where the sun is close to the ellipse, the shaded area is defined by 2 short radii and a long distance of arc on the perimeter of the ellipse. At the other end, the shaded area is defined by 2 long radii and a short distance of arc on the perimeter of the ellipse.
The diagram above shows the distance traveled by a planet at two different intervals in
its solar orbit. The astronomer Johannes Kepler compared the two shaded gray areas of
the ellipse in order to determine the:
- mass of planets with different orbital periods.
- diameter of the orbits of other planets.
- gravitational pull that the planet exerts on other objects.
- changing speeds at which a planet orbits the sun.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
D. This question requires the examinee to recognize the law developed by
Johannes Kepler to describe the changing orbital speed of a planet as it travels around
the sun. This law states that the orbital speed of a planet varies so that a line joining
the sun and the planet will sweep over equal areas in equal time intervals. The graphic
in the question represents the two equal areas that a hypothetical planet covers during
two different but equal time periods in its elliptical orbit. Since the time periods are
the same, but the distance covered during the two intervals is different, the orbital speed
must be different.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the physical characteristics of the moon and Earth, including theories on their origin and the evidence used to support those theories.
- Analyze the interactions of the sun, moon, and Earth, including the effects of these interactions on Earth systems and the evolution of the sun-moon-Earth system.
- Analyze the apparent motions of stars and planets relative to Earth, and the characteristics of the celestial sphere.
Sample Item:
The large dark areas of the moon known as mares are easily visible from Earth. Which of
the following explains the presence of these dark areas?
- Massive volcanic eruptions emptied underlying magma caverns, causing their collapse
and the formation of calderas.
- Shortly after the moon's formation, Earth's strong gravitational pull on the moon caused
the release of magma from fissures in the crust.
- Large meteorites excavated huge craters that filled with low-viscosity basalt flowing
from the fractures created in the underlying crust.
- When the moon was still semi-molten, thin areas of crust collapsed due to tectonic
activity, creating low areas that trapped sediments.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
C. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the
physical characteristics of the moon. The mares on the moon are large dark areas that
formed when meteorites slammed into the moon, producing huge craters that then filled
with basalt that flowed up into the craters through fractures in the moon's crust.

